Mattermost installation
This tutorial shows the basic concepts of Capact on the Mattermost installation example.
Goal
This instruction will guide you through the installation of Mattermost on a Kubernetes cluster using Capact.
Mattermost depends on the PostgreSQL database. Depending on the cluster configuration, with the Capact project, you can install Mattermost with a managed Cloud SQL, AWS RDS database or a locally deployed PostgreSQL Helm chart.
The diagrams below show possible scenarios:
Install all Mattermost components in a Kubernetes cluster
Install Mattermost with an external Cloud SQL database
Prerequisites
- Capact CLI installed.
kubectlinstalled.- Cluster with Capact installation. See the installation tutorial.
- Helm Storage installed and configured. See the installation and usage instructions.
- For the scenario with Cloud SQL, access to Google Cloud Platform.
Install all Mattermost components in a Kubernetes cluster
By default, the Capact Engine Global Policy prefers Kubernetes solutions.
interface:
rules: # Configures the following behavior for Engine during rendering Action
- interface:
path: cap.*
oneOf:
- implementationConstraints: # prefer Implementation for Kubernetes
requires:
- path: "cap.core.type.platform.kubernetes"
# any revision
- implementationConstraints: {} # fallback to any Implementation
As a result, all external solutions, such as Cloud SQL, have a lower priority, and they are not selected. The below scenario shows how to install Mattermost with a locally deployed PostgreSQL Helm chart.
Instructions
Create a Kubernetes Namespace:
export NAMESPACE=local-scenario
kubectl create namespace $NAMESPACEList all Interfaces:
capact hub interfaces getPATH LATEST REVISION IMPLEMENTATIONS
+---------------------------------------------------------+-----------------+-----------------------------------------------------------------+
cap.interface.analytics.elasticsearch.install 0.1.0 cap.implementation.elastic.elasticsearch.install
cap.implementation.aws.elasticsearch.provision
+---------------------------------------------------------+-----------------+-----------------------------------------------------------------+
cap.interface.automation.concourse.change-db-password 0.1.0 cap.implementation.concourse.concourse.change-db-password
+---------------------------------------------------------+-----------------+-----------------------------------------------------------------+
cap.interface.automation.concourse.install 0.1.0 cap.implementation.concourse.concourse.install
+---------------------------------------------------------+-----------------+-----------------------------------------------------------------+
cap.interface.aws.elasticsearch.provision 0.1.0 cap.implementation.aws.elasticsearch.provision
+---------------------------------------------------------+-----------------+-----------------------------------------------------------------+
cap.interface.aws.rds.postgresql.provision 0.1.0 cap.implementation.aws.rds.postgresql.provision
+---------------------------------------------------------+-----------------+-----------------------------------------------------------------+
cap.interface.database.postgresql.install 0.1.0 cap.implementation.bitnami.postgresql.install
cap.implementation.aws.rds.postgresql.install
cap.implementation.gcp.cloudsql.postgresql.install
cap.implementation.gcp.cloudsql.postgresql.install
+---------------------------------------------------------+-----------------+-----------------------------------------------------------------+The table represents all available Actions that you can execute on this Capact. There is also a list of the Implementations available for a given Interface. You can see, that for the
cap.interface.database.postgresql.installwe have:- a Kubernetes deployment using the Bitnami Helm chart,
- an AWS RDS instance,
- a GCP Cloud SQL instance.
Create an Action with the
cap.interface.productivity.mattermost.installInterface:Create input parameters for the Action, where you provide the ingress host for the Mattermost.
cat <<EOF > /tmp/mattermost-install.yaml
input-parameters:
host: mattermost.capact.local
EOFNOTE: The host must be in a subdomain of the Capact domain, so the ingress controller and Cert Manager can handle the Ingress properly it.
If you use a local Capact installation, then you have to add an entry in
/etc/hostsfor it e.g.:127.0.0.1 mattermost.capact.localcapact action create -n $NAMESPACE --name mattermost-install cap.interface.productivity.mattermost.install --parameters-from-file /tmp/mattermost-install.yamlGet the status of the Action from the previous step:
capact action get -n $NAMESPACE mattermost-installNAMESPACE NAME PATH RUN STATUS AGE
+--------------+--------------------+-----------------------------------------------+-------+--------------+-----+
gcp-scenario mattermost-install cap.interface.productivity.mattermost.install false READY_TO_RUN 19s
+--------------+--------------------+-----------------------------------------------+-------+--------------+-----+In the
STATUScolumn you can see the current status of the Action. When the Action workflow is being rendered by the Engine, you will see theBEING_RENDEREDstatus. After the Action finished rendering and the status isREADY_TO_RUN, you can go to the next step.note
To automatically wait for
READY_TO_RUN, run:capact act wait --for=phase=READY_TO_RUN -n $NAMESPACE mattermost-installRun the rendered Action:
After the Action is in
READY_TO_RUNstatus, you can run it. To do this, execute the following command:capact action run -n $NAMESPACE mattermost-installCheck the Action execution and wait till it is finished:
capact action watch -n $NAMESPACE mattermost-installGet the ID of the
cap.type.productivity.mattermost.configTypeInstance:capact action get -n $NAMESPACE mattermost-install -ojsonpath -t '{.Actions[*].output.typeInstances[?(@.typeRef.path == "cap.type.productivity.mattermost.config")].id}'Get the TypeInstance value:
Use the ID from the previous step and fetch the TypeInstance value:
capact typeinstance get {type-instance-id} -ojsonpath -t '{[0].latestResourceVersion.spec.value}'Open the Mattermost console using the host from the TypeInstance value, you got in the previous step.
🎉 Hooray! You now have your own Mattermost instance installed. Be productive!
Clean-up
⚠️ CAUTION: This removes all resources that you created.
When you are done, remove the Action and Helm charts:
capact action delete -n $NAMESPACE mattermost-install
helm delete -n $NAMESPACE $(helm list -f="mattermost-*|postgresql-*" -q -n $NAMESPACE)
Install Mattermost with an external CloudSQL database
To change the Mattermost installation, we need to adjust our Global policy to prefer GCP solutions. Read more about Global policy configuration here.
Instructions
Create a TypeInstance with GCP Service Account.
Follow the GCP Service Account TypeInstance creation guide to create and obtain ID of the newly created TypeInstance.
Export the TypeInstance ID as environment variable:
export TI_ID={GCP Service Account TypeInstance ID}
Export Helm storage TypeInstances, which were created as a part of prerequisite instructions:
export HELM_TEMPLATE_STORAGE_ID={id}
export HELM_RELEASE_STORAGE_ID={id}Update the Global Policy:
cat > /tmp/policy.yaml << ENDOFFILE
interface:
default:
inject:
requiredTypeInstances:
- description: Helm template
id: ${HELM_TEMPLATE_STORAGE_ID}
- description: Helm release
id: ${HELM_RELEASE_STORAGE_ID}
rules:
- interface:
path: cap.interface.database.postgresql.install
oneOf:
- implementationConstraints:
attributes:
- path: "cap.attribute.cloud.provider.gcp"
requires:
- path: "cap.type.gcp.auth.service-account"
inject:
requiredTypeInstances:
- id: ${TI_ID}
description: "GCP Service Account"
- interface:
path: cap.*
oneOf:
- implementationConstraints:
requires:
- path: "cap.core.type.platform.kubernetes"
- implementationConstraints: {} # fallback to any Implementation
ENDOFFILEcapact policy apply -f /tmp/policy.yamlNOTE: If you are not familiar with the policy syntax above, check the policy overview document.
Create a Kubernetes Namespace:
export NAMESPACE=gcp-scenario
kubectl create namespace $NAMESPACEInstall Mattermost with the new Global Policy:
The Global Policy was updated to prefer GCP solutions for the PostgreSQL Interface. As a result, during the render process, the Capact Engine will select a Cloud SQL Implementation which is available in our Hub server.
Repeat the steps 4–11 from Install all Mattermost components in a Kubernetes cluster in the
gcp-scenarioNamespace.
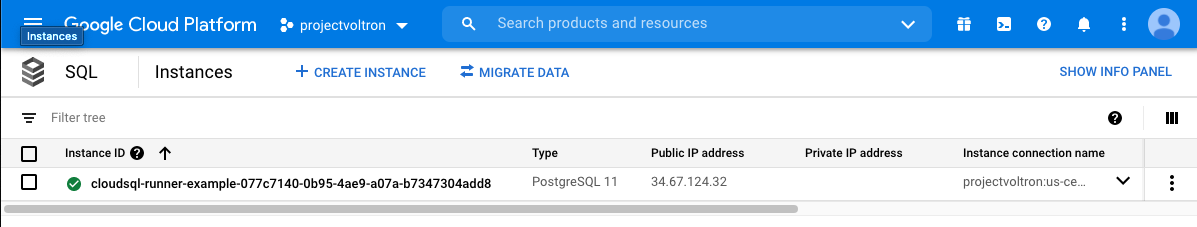
🎉 Hooray! You now have your own Mattermost instance installed. Be productive!
Clean-up
⚠️ CAUTION: This removes all resources that you created.
When you are done, remove the Cloud SQL manually and delete the Action:
kubectl delete action mattermost-instance -n $NAMESPACE
helm delete -n $NAMESPACE $(helm list -f="mattermost-*" -q -n $NAMESPACE)
Install Mattermost with an external AWS RDS database
To change the Mattermost installation, we need to adjust our Global policy to prefer AWS solutions. Read more about Global policy configuration here.
Instructions
Create AWS Credentials TypeInstance.
Follow the AWS Credentials TypeInstance creation guide to create and obtain ID of the newly created TypeInstance.
Export the TypeInstance ID as environment variable:
export TI_ID={AWS credentials TypeInstance ID}
Export Helm storage TypeInstances, which were created as a part of prerequisite instructions:
export HELM_TEMPLATE_STORAGE_ID={id}
export HELM_RELEASE_STORAGE_ID={id}Update the Global Policy:
cat > /tmp/policy.yaml << ENDOFFILE
interface:
default:
inject:
requiredTypeInstances:
- description: Helm template
id: ${HELM_TEMPLATE_STORAGE_ID}
- description: Helm release
id: ${HELM_RELEASE_STORAGE_ID}
rules:
- interface:
path: cap.interface.database.postgresql.install
oneOf:
- implementationConstraints:
attributes:
- path: "cap.attribute.cloud.provider.aws"
inject:
requiredTypeInstances:
- id: ${TI_ID}
description: "AWS credentials"
- interface:
path: cap.*
oneOf:
- implementationConstraints:
requires:
- path: "cap.core.type.platform.kubernetes"
- implementationConstraints: {} # fallback to any Implementation
ENDOFFILEcapact policy apply -f /tmp/policy.yamlNOTE: If you are not familiar with the policy syntax above, check the policy overview document.
Create a Kubernetes Namespace:
export NAMESPACE=aws-scenario
kubectl create namespace $NAMESPACEInstall Mattermost with the new Global Policy:
The Global Policy was updated to prefer AWS solutions for the PostgreSQL Interface. As a result, during the render process, the Capact Engine will select a Cloud SQL Implementation which is available in our Hub server.
Repeat the steps 4–11 from Install all Mattermost components in a Kubernetes cluster in the
aws-scenarioNamespace.
🎉 Hooray! You now have your own Mattermost instance installed. Be productive!
Clean-up
⚠️ CAUTION: This removes all resources that you created.
When you are done, remove the AWS RDS manually and delete the Action:
kubectl delete action mattermost-instance -n $NAMESPACE
helm delete -n $NAMESPACE $(helm list -f="mattermost-*" -q -n $NAMESPACE)
Behind the scenes
The following section extends the tutorial with additional topics, to let you dive even deeper into the Capact concepts.
OCF manifests
A user consumes content stored in Capact Hub. The content is defined using Open Capability Format (OCF) manifests. The OCF specification defines the shape of manifests that Capact understands, such as Interface or Implementation.
To see all the manifest that Hub stores, navigate to the Hub content structure.
To see the Mattermost installation manifests, click on the following links:
- Mattermost installation Interface — a generic description of Mattermost installation (action name, input, and output — a concept similar to interfaces in programming languages),
- Mattermost installation Implementation — represents the dynamic workflow for Mattermost Installation.
Content development
To make it easier to develop new Hub content, we implemented a dedicated CLI. Currently, it exposes the validation feature for OCF manifests. It detects the manifest kind and the OCF version to properly validate a given file. You can use it to validate one or multiple files at a single run.
To validate all Hub manifests, navigate to the repository root directory and run the following command:
capact validate ./manifests/**/*.yaml
In the future, we plan to extend the Capact CLI with additional features, such as:
- manifests scaffolding,
- manifests submission,
- signing manifests.
Additional resources
If you want to learn more about the project, check the capact repository.
To learn how to develop content, get familiar with the content development guide.

