Guide
Introduction
This guide shows the first steps on how to develop OCF content for Capact. We will show how to:
- define new Types and Interfaces,
- create Implementation for the Interfaces,
- use other Interfaces in your Implementations,
- test the new manifests on a local development Capact cluster.
As an example, we will create OCF manifests to deploy Mattermost with a PostgreSQL database.
Prerequisites
To develop and test the created content, you will need to have a Capact environment. To set up a local environment, install the following prerequisites:
Populator - download the binary from the latest Capact release
During the actual Capact installation step, provide additional flag for
capact installcommand:capact install --capact-overrides=hub-public.populator.enabled=falseHelm storage backend installed on the Capact cluster
Also, clone the repository with the Capact manifests:
git clone [email protected]:capactio/hub-manifests.git
Some other materials worth reading before are:
- Mattermost installation tutorial - Learn how to execute actions in Capact.
- Argo Workflows documentation - Capact action syntax is based on Argo workflows, so it's highly recommended you understand what is Argo and how to create Argo workflows.
- Capact runners - Understand, what are Capact runners.
- Capact CLI validate command - Learn how to validate your manifests syntax.
Types, Interfaces and Implementations
If you have some software development experience, concepts like types and interfaces should be familiar to you. In Capact, Types represent different objects in the environment. These could be database or application instances, servers, but also more abstract things, like an IP address or hostname. An actual object of a Type is called a TypeInstance.
Interfaces are operations, which can be executed on certain Types. Let's say we have a Type called postgresql.config, which represents a PostgreSQL database instance. We could have an Interface postgresql.install, which will provision a PostgreSQL instance and create a TypeInstance of postgresql.config.
Interfaces can be grouped into InterfaceGroups. InterfaceGroups are used to logically group the Interfaces. This is mostly used for presentation purposes, like to show the user all Interfaces, which operate on PostgreSQL instances. So if you have two Interfaces: postgresql.install and postgresql.uninstall, you can group them into postgresql InterfaceGroup.
Of course, there are multiple ways to create a PostgreSQL instance: you can create it on a public cloud or on-premise, and you could deploy it as a virtual machine or as a Kubernetes StatefulSet. To cover these scenarios, Capact allows defining multiple Implementations of some Interfaces. For example:
aws.postgresql.installImplementation of thepostgresql.installInterface will deploy AWS RDS instances, whereasbitnami.postgresql.installImplementation will deploy a PostgreSQL Helm chart on Kubernetes.
Define your Types and Interfaces
Let's try to create manifests required to define a capability to install Mattermost server. We will need to create the following entities:
mattermost.configType - Represents a Mattermost server.mattermost.install-inputType - Represents input parameters needed to install a Mattermost server.mattermostInterfaceGroup - Groups Interfaces from themattermostgroup, e.g. if you havemattermost.installandmattermost.upgradeInterfaces.mattermost.installInterface - An operation, which installs Mattermost servers. You can think of it as a function:mattermost.install(mattermost.install-input) -> mattermost.config
NOTE: To simplify and speed up the process of creating the manifests, you can use Capact Manifest Generator in the Capact CLI. You can read more about it in this document.
Create the Interface Group manifest
First, we need to create an InterfaceGroup manifest, which groups Interfaces corresponding to some application.
Let's create a InterfaceGroup called cap.interface.productivity.mattermost, which will group Interfaces operating on Mattermost instances.
In manifests/interface/productivity/, create a file called mattermost.yaml, with the following content:
manifests/interface/productivity/mattermost.yaml
ocfVersion: 0.0.1
revision: 0.1.0
kind: InterfaceGroup
metadata:
prefix: cap.interface.productivity
name: mattermost
displayName: "Mattermost"
description: "Mattermost is an open source collaboration tool for developers."
documentationURL: https://docs.mattermost.com/
supportURL: https://docs.mattermost.com/
iconURL: https://storage.googleapis.com/dashboard-icons/mattermost.svg
maintainers:
- email: [email protected]
name: your-name
url: your-website
Create the Interface manifest
After we have the InterfaceGroup, let's create the Interface for installing Mattermost.
Create the directory manifests/interface/productivity/mattermost.
Inside this directory, create a file install.yaml with the following content:
manifests/interface/productivity/mattermost/install.yaml
ocfVersion: 0.0.1
revision: 0.1.0
kind: Interface
metadata:
prefix: cap.interface.productivity.mattermost
name: install
displayName: "Install Mattermost Team Edition"
description: "Install action for Mattermost Team Edition"
documentationURL: https://docs.mattermost.com/
supportURL: https://docs.mattermost.com/
iconURL: https://docs.mattermost.com/_static/images/Mattermost-Logo-Blue.svg
maintainers:
- email: [email protected]
name: your-name
url: your-website
spec:
input:
parameters: # the Interface requires `input-parameters` of Type "cap.type.productivity.mattermost.install-input"
input-parameters:
typeRef:
path: cap.type.productivity.mattermost.install-input
revision: 0.1.0
output:
typeInstances: # the Interface outputs TypeInstance of Type "cap.type.productivity.mattermost.config"
mattermost-config:
typeRef:
path: cap.type.productivity.mattermost.config
revision: 0.1.0
The spec.input property defines inputs, required by the Interface. There are two types of inputs:
spec.input.parameters- User provided input parameters, i.e. these could be configuration parameters required by the operation,spec.input.typeInstances- input TypeInstances, i.e. a PostgreSQL database, which is needed for an application.
The spec.output property defines the TypeInstance, which this Interface returns.
Although Mattermost needs a database, we don't specify it as an input argument here. That is because, we leave selecting a database to the Implementation.
Create the Type manifests
Now we need to define the two Types, which we use in our Interface: cap.type.productivity.mattermost.install-input and cap.type.productivity.mattermost.config.
manifests/type/productivity/mattermost/install-input.yaml
ocfVersion: 0.0.1
revision: 0.1.0
kind: Type
metadata:
name: install-input
prefix: cap.type.productivity.mattermost
displayName: "Mattermost install input"
description: Defines installation parameters for Mattermost
documentationURL: https://docs.mattermost.com/
supportURL: https://docs.mattermost.com
maintainers:
- email: [email protected]
name: your-name
url: your-website
spec:
jsonSchema:
value: |-
{
"$schema": "http://json-schema.org/draft-07/schema",
"type": "object",
"title": "Mattermost installation parameters",
"required": [
"host"
],
"definitions": {
"hostname": {
"type": "string",
"format": "hostname",
"title": "Hostname"
}
},
"properties": {
"host": {
"$ref": "#/definitions/hostname"
}
},
"additionalProperties": true
}
manifests/type/productivity/mattermost/config.yaml
ocfVersion: 0.0.1
revision: 0.1.0
kind: Type
metadata:
name: config
prefix: cap.type.productivity.mattermost
displayName: Mattermost config
description: Defines configuration for Mattermost instance
documentationURL: https://docs.mattermost.com/
supportURL: https://docs.mattermost.com/
iconURL: https://docs.mattermost.com/_static/images/Mattermost-Logo-Blue.svg
maintainers:
- email: [email protected]
name: your-name
url: your-website
spec:
jsonSchema:
value: |-
{
"$schema": "http://json-schema.org/draft-07/schema",
"type": "object",
"title": "The schema for Mattermost configuration",
"required": [
"version"
],
"definitions": {
"semVer": {
"type": "string",
"minLength": 5,
"pattern": "^(0|[1-9]\\d*)\\.(0|[1-9]\\d*)\\.(0|[1-9]\\d*)(?:-((?:0|[1-9]\\d*|\\d*[a-zA-Z-][0-9a-zA-Z-]*)(?:\\.(?:0|[1-9]\\d*|\\d*[a-zA-Z-][0-9a-zA-Z-]*))*))?(?:\\+([0-9a-zA-Z-]+(?:\\.[0-9a-zA-Z-]+)*))?$",
"title": "Semantic Versioning version",
"examples": [
"1.19.0",
"2.0.1-alpha1"
]
},
"hostname": {
"type": "string",
"format": "hostname",
"title": "Hostname"
}
},
"properties": {
"version": {
"$ref": "#/definitions/semVer"
},
"host": {
"$ref": "#/definitions/hostname"
}
},
"additionalProperties": true
}
The Type values are described using JSON Schema and are used to validate the data of the inputs and outputs.
Runners
The Action execution is handled by runners. Currently, we provide the following runners:
- Argo Workflow Runner
- Helm Runner
- Terraform Runner
- CloudSQL Runner (deprecated in favor of Terraform Runner)
To check the schema of the runner input, you have to look in the manifests/type/runner directory. You can find there the JSON schema and an example input for the runner.
You can read more about runners in this document.
Write the Implementation for the Interface
The syntax used to describe the workflows in Implementations is based on Argo Workflows. It's highly recommended you read their documentation and understand what is Argo and how to create Argo workflows, before writing OCF Implementations.
After we defined the Interfaces, and the Types, we can write an Implementation of mattermost.install. Our Implementation will use a PostgreSQL database, which will be provided by another Interface, which is already available in Capact. We also allow users to provide his own PostgreSQL instance TypeInstance.
Create a file manifests/implementation/mattermost/mattermost-team-edition/install.yaml with the following content:
manifests/implementation/mattermost/mattermost-team-edition/install.yaml
ocfVersion: 0.0.1
revision: 0.1.0
kind: Implementation
metadata:
prefix: cap.implementation.mattermost.mattermost-team-edition
name: install
displayName: Install Mattermost Team Edition
description: Action which installs Mattermost Team Edition via Helm chart
documentationURL: https://docs.mattermost.com/
supportURL: https://docs.mattermost.com/
license:
name: "Apache 2.0"
maintainers:
- email: [email protected]
name: your-name
url: your-website
spec:
appVersion: "10,11,12,13"
outputTypeInstanceRelations:
mattermost-config:
uses:
- mattermost-helm-release
- postgresql
- database
- database-user
additionalInput:
typeInstances:
postgresql:
typeRef:
path: cap.type.database.postgresql.config
revision: 0.1.0
verbs: ["get"]
parameters:
additional-parameters:
typeRef:
path: cap.type.mattermost.helm.install-input
revision: 0.1.0
implements:
- path: cap.interface.productivity.mattermost.install
revision: 0.1.0
requires:
cap.core.type.platform:
oneOf:
- name: kubernetes
revision: 0.1.0
cap.core.type.hub.storage: # Helm storage needs to be present as a prerequisite for this Implementation
allOf:
- name: cap.type.helm.release.storage
revision: 0.1.0
alias: helm-release-storage
- name: cap.type.helm.template.storage
revision: 0.1.0
alias: helm-template-storage
imports:
- interfaceGroupPath: cap.interface.runner.helm
alias: helm
methods:
- name: install
revision: 0.1.0
- interfaceGroupPath: cap.interface.runner.argo
alias: argo
methods:
- name: run
revision: 0.1.0
- interfaceGroupPath: cap.interface.templating.jinja2
alias: jinja2
methods:
- name: template
revision: 0.1.0
- interfaceGroupPath: cap.interface.database.postgresql
alias: postgresql
methods:
- name: install
revision: 0.1.0
- name: create-db
revision: 0.1.0
- name: create-user
revision: 0.1.0
action:
runnerInterface: argo.run
args:
workflow:
entrypoint: mattermost-install
templates:
- name: mattermost-install
inputs:
artifacts:
- name: input-parameters
- name: postgresql
optional: true
- name: additional-parameters
optional: true
outputs:
artifacts:
- name: mattermost-config
from: "{{steps.resolve-ti-value.outputs.artifacts.ti-artifact}}"
steps:
# Install DB
- - name: install-db
capact-when: postgresql == nil
capact-action: postgresql.install
capact-outputTypeInstances:
- name: postgresql
from: postgresql
backend: helm-template-storage
arguments:
artifacts:
- name: input-parameters
raw:
data: |
superuser:
username: superuser
defaultDBName: postgres
- - name: create-user
capact-action: postgresql.create-user
capact-outputTypeInstances:
- name: database-user
from: user
arguments:
artifacts:
- name: postgresql
from: "{{steps.install-db.outputs.artifacts.postgresql}}"
- name: input-parameters
raw:
data: |
name: mattermost
- - name: render-create-db-args
capact-action: jinja2.template
arguments:
artifacts:
- name: template
raw:
data: |
name: mattermost
owner: "<@ name @>"
- name: input-parameters
from: "{{steps.create-user.outputs.artifacts.user}}"
- name: configuration
raw:
data: "unpackValue: true"
- - name: create-db
capact-action: postgresql.create-db
capact-outputTypeInstances:
- name: database
from: database
arguments:
artifacts:
- name: postgresql
from: "{{steps.install-db.outputs.artifacts.postgresql}}"
- name: input-parameters
from: "{{steps.render-create-db-args.outputs.artifacts.render}}"
- - name: prepare-parameters
template: prepare-parameters
arguments:
artifacts:
- name: input-parameters
from: "{{inputs.artifacts.input-parameters}}"
- name: additional-parameters
from: "{{inputs.artifacts.additional-parameters}}"
optional: true
- name: psql
from: "{{steps.install-db.outputs.artifacts.postgresql}}"
- name: db
from: "{{steps.create-db.outputs.artifacts.database}}"
- name: user
from: "{{steps.create-user.outputs.artifacts.user}}"
# Install Mattermost
- - name: create-helm-args
capact-action: jinja2.template
arguments:
artifacts:
- name: template
raw:
data: |
generateName: true
chart:
name: "mattermost-team-edition"
repo: "https://helm.mattermost.com"
version: "4.0.0"
values:
ingress:
enabled: true
path: "/"
annotations:
"cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer": letsencrypt
hosts:
- <@ input.host | default("mattermost.example.com") @>
tls:
- hosts:
- <@ input.host | default("mattermost.example.com") @>
secretName: mattermost-team-edition-tls-<@ random_word(length=5) @>
externalDB:
enabled: true
externalDriverType: "postgres"
externalConnectionString: "postgres://<@ user.name @>:<@ user.password @>@<@ psql.host @>:<@ psql.port @>/<@ db.name @>?sslmode=disable"
mysql:
enabled: false
output:
helmRelease:
useHelmReleaseStorage: true
additional:
useHelmTemplateStorage: true
goTemplate: |
host: "{{ index .Values.ingress.hosts 0 }}"
version: "{{ .Values.image.tag }}
- name: input-parameters
from: "{{steps.prepare-parameters.outputs.artifacts.merged}}"
- name: configuration
raw:
data: "unpackValue: true"
- - name: helm-install
capact-action: helm.install
capact-outputTypeInstances:
- name: mattermost-helm-release
from: helm-release
backend: helm-release-storage
arguments:
artifacts:
- name: input-parameters
from: "{{steps.create-helm-args.outputs.artifacts.render}}"
- name: runner-context
from: "{{workflow.outputs.artifacts.runner-context}}"
# allows reusing this workflow as a part of other umbrella workflows and read the artifact value
- - name: resolve-ti-value
template: resolve-ti-art-value
capact-outputTypeInstances:
- name: mattermost-config
from: ti-artifact
backend: helm-template-storage
arguments:
artifacts:
- name: ti-artifact
from: "{{steps.helm-install.outputs.artifacts.additional}}"
- name: backend
from: "{{workflow.outputs.artifacts.helm-template-storage}}"
- name: prepare-parameters
inputs:
artifacts:
- name: input-parameters
path: /yamls/input.yaml
- name: additional-parameters
path: /yamls/additionalinput.yaml
optional: true
- name: psql
path: /yamls/psql.yaml
- name: db
path: /yamls/db.yaml
- name: user
path: /yamls/user.yaml
container:
image: ghcr.io/capactio/infra/merger:2ada6f8
outputs:
artifacts:
- name: merged
path: /merged.yaml
- name: resolve-ti-art-value
inputs:
artifacts:
- name: ti-artifact
path: /tmp/input-ti.yaml
- name: backend
path: /tmp/storage-backend.yaml
outputs:
artifacts:
- name: ti-artifact
path: /tmp/output.yaml
container:
image: ghcr.io/capactio/ti-value-fetcher:2ada6f8
env:
- name: APP_LOGGER_DEV_MODE
value: "true"
- name: APP_INPUT_TI_FILE_PATH
value: "{{inputs.artifacts.ti-artifact.path}}"
- name: APP_INPUT_BACKEND_TI_FILE_PATH
value: "{{inputs.artifacts.backend.path}}"
- name: APP_OUTPUT_FILE_PATH
value: "{{outputs.artifacts.ti-artifact.path}}"
Let's take a look on the Implementation YAML. Implementation has the following properties in the spec property:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
appVersion | Application versions, which this Implementation supports. |
outputTypeInstanceRelations | Specifies all output TypeInstances to upload to Hub with theirs relationships between them. Only the TypeInstances created in this Implementation have to be mentioned here. If a TypeInstances in created in another action and brought into the context with capact-outputTypeInstances, then it should not be defined here. |
additionalInput | Additional input for the Implementation, compared to the Interface. In our case, here we define the postgresql.config, as our Implementation uses a PostgreSQL instance for Mattermost. The additional parameter helm.install-input is used to specify optional overrides for Helm Chart values used by this implementation. |
additionalOutput | This section defines any additional TypeInstances, which are created in the Implementation, compared to the Interface. We don't make use of that in our example. |
implements | Defines which Interfaces are implemented by this Implementation. |
requires | List of system prerequisites that need to be present in the environment managed by Capact to use this Implementation. In our example, we will deploy Mattermost as a Helm chart on Kubernetes, which means we need a Kubernetes cluster. Requirement items can specify alias and be used inside workflow under {{workflow.outputs.artifacts.{alias}}}, where {alias-name} is the alias. A TypeInstance with alias is injected into the workflow based on Policy configuration. To learn more, see the TypeInstance Injection paragraph in Policy Configuration document. |
imports | Here we define all other Interfaces, we use in our Implementation. We can then refer to them as '<alias>.<method-name>'. |
action | Holds information about the actions that is executed. In the case of the Argo workflow Runner, in this section we define the Argo workflow, which is executed in this Implementation. |
You can notice, that
mattermost-config(which is theadditionaloutput TypeInstance fromhelm.install) is defined in theoutputTypeInstanceRelations, although it was created inhelm.install. Theadditionalfromhelm.installis specially, becausehelm.installdoes not know the Type of TypeInstances, so it's not defined inhelm.installImplementation, but must be defined in the caller Implementation. In the future, we will improve the syntax, so it will be more clear, which TypeInstances need a separate entry inoutputTypeInstanceRelationsand which don't.
The workflow syntax is based on Argo Workflows, with a few extensions introduced by Capact. These extensions are:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
.templates.steps[][].capact-when | Allows for conditional execution of a step, based on an expression with an input workflow artifacts arguments. You can make assertions on artifacts defined under inputs.arguments.artifacts for a given template. It supports the syntax defined here: antonmedv/expr. |
.templates.steps[][].capact-action | Allows to import another Interface. In our example, we use this to provision PostgreSQL with postgresql.install Interface. |
.templates.steps[][].capact-policy | Allows defining Workflow step policy. |
.templates.steps[][].capact-outputTypeInstance | A list of TypeInstances, from the called action, which are brought into the context of this Implementations. The from property must match the name of the output from the called Action. You can then use it in the Implementations outputTypeInstanceRelations, when defining relations between TypeInstances. The optional backend property specifies where to store the TypeInstance data. Read more about storage backend in the Using custom backend storage section. |
.templates.steps[][].capact-updateTypeInstance | A list of TypeInstances, from the called action, which are brought into the context of this Implementations and will be used to update existing TypeInstance. The from property must match the name of the output from the called Action. The optional backend property specifies where to store the TypeInstance data. Read more about storage backend in the Using custom backend storage section. |
Let's go through the Implementation and try to understand, what is happening in each step of the action. Our Mattermost installation uses a PostgreSQL database. We defined an additional input postgresql of type cap.type.database.postgresql.config. Additional inputs are optional, so we need to handle the scenario, where no TypeInstance for postgresql was provided. The first workflow step install-db is conditionally using the postgresql.install Interface to create an PostgreSQL instance.
The
input-parametersforpostgresql.installare hardcoded in this example. In a real workflow, they should be generated or taken from theinput-parametersfor this Implementation.
When using an Action step you can also provide a Workflow step policy, to enforce, that a given Implementation will be selected. For example, to enforce that the PostgreSQL will be deployed using Bitnami Helm chart, you could use:
- - capact-action: postgresql.install
name: install-db
capact-when: postgresql == nil
capact-policy:
interface:
rules:
- interface:
path: cap.interface.database.postgresql.install
oneOf:
- implementationConstraints:
path: "cap.implementation.bitnami.postgresql.installYou can read more about policies on the Policy overview page.
In the next step we are creating a database for the Mattermost server. If you look at the Interface definition of cap.interface.database.postgresql.create-db, you will see, that it requires a postgresql TypeInstance of Type cap.type.database.postgresql.config and input parameters cap.type.database.postgresql.database-input, and outputs a database TypeInstance of Type cap.type.database.postgresql.database. The render-create-db-args renders input parameters for postgresql.install Interface. In the create-db step, we are providing the inputs to the Interface via the .arguments.artifacts field. We also have to map the output of this step to our output definitions in additionalOutput and the implemented Interface in the capact-outputTypeInstances field.
The create-helm-args step is used to prepare the input parameters for the helm.install Interface. Jinja template engine is used here to render the Helm runner arguments with the required data from the postgresql and database TypeInstances. This step doesn't create any TypeInstances and serves only the purpose of creating the input parameters for the Helm runner.
You can check the schema of the Helm runner args in the Type manifest.
NOTE: To create the input parameters for
helm.installwe have to use data from two artifacts. As thejinja.templateInterface consumes a Jinja2 template and a single variable input, we introduced merger container. that merges multiple inputs to a single artifact. It is used in theprepare-parametersstep. You can read more about merger here.
The last step launches the Helm runner, deploys the Mattermost server and creates the mattermost-config and mattermost-helm-release TypeInstances. The mattermost-config TypeInstance data was provided by the Helm runner in the additional output artifacts from this step. Check the Helm runner documentation, on how the additional output is created.
Note the runner-context argument, which provided the context for the runner. Capact Engine injects a global artifact workflow.outputs.artifacts.runner-context into the workflow, so if you use a runner, which needs the runner context, you can to do it using:
arguments:
artifacts:
- name: runner-context
from: "{{workflow.outputs.artifacts.runner-context}
To verify, if a runner needs the context, check the Interface of the runner (e.g. Interface for Helm runner).
Using custom storage backend
By default, Capact used the default storage backend which stores static TypeInstance values inside Local Hub database. However, you can use a custom backend - for example, to store and manage TypeInstance values externally. The available storage backends are listed here.
To enforce using a given storage backend for Implementation, use the Implementation.requires property:
requires:
cap.type.aws.secrets-manager:
allOf:
- typeRef:
path: storage
revision: 0.1.0
alias: aws-storage
The Implementation which uses that section cannot be run unless the cap.type.aws.secrets-manager.storage is installed and injected into the Implementation workflow. The aws-storage is an alias for the injected backend storage, and you can refer it inside the workflow.
To read how to inject such TypeInstance while running Capact Action, see the Policy Overview document.
Then, refer the storage backend in the capact-outputTypeInstance or capact-updateTypeInstances properties, to upload such artifacts:
capact-outputTypeInstances:
- name: example-artifact
from: example-artifact
backend: aws-storage # use TypeInstance injected from the `requires` property
You can read more about the storage backends feature here.
Workflow artifacts data shape
While building Implementation workflows, you need to make sure the Argo artifacts specified under the capact-outputTypeInstances property, have a proper shape, to be able to upload them as output TypeInstances.
The shape of the artifact depends on used storage backend:
If a given storage backend accepts a static value (for example, the default one), the artifact must contain
valueproperty, which holds the static data:value: # anything - object, number, string, array...
foo: barExample storage backends:
- default (Local Hub database)
- AWS Secrets Manager
If a given storage backend accepts just
context, that is, the backend-specific metadata, the artifact must contain thebackend.contextproperty:backend:
context:
foo: barThe context is validated against the Storage backend context schema while creating TypeInstance at the end of the Capact Action run.
Some upper-level workflows may require data fetched from such backend within the same workflow which produces such TypeInstance. To enable that, Content Developer should use TypeInstance Value Fetcher container to resolve value based on the context data:
TypeInstance Value Fetcher example usage
# (...)
# produce helm-release TypeInstance with just `backend.context`
- - name: helm-install
template: helm-install
arguments:
artifacts:
- name: input-parameters
from: "{{inputs.artifacts.input-parameters}}"
- name: runner-context
from: "{{inputs.artifacts.runner-context}}"
- name: kubeconfig
from: "{{inputs.artifacts.kubeconfig}}"
# resolve `value` against the helm release storage backend based on `backend.context`
- - name: resolve-helm-rel-value
template: resolve-ti-art-value
capact-outputTypeInstances: # register "full" artifact with both `value` and `backend.context` as an output
- name: helm-release
from: ti-artifact
backend: helm-release-storage
arguments:
artifacts:
- name: ti-artifact
from: "{{steps.helm-install.outputs.artifacts.helm-release}}"
- name: backend
from: "{{workflow.outputs.artifacts.helm-release-storage}}"
# TypeInstance Value Fetcher template
- name: resolve-ti-art-value
inputs:
artifacts:
- name: ti-artifact
path: /tmp/input-ti.yaml
- name: backend
path: /tmp/storage-backend.yaml
outputs:
artifacts:
- name: ti-artifact
path: /tmp/output.yaml
container:
image: ghcr.io/capactio/ti-value-fetcher:2ada6f8
env:
- name: APP_LOGGER_DEV_MODE
value: "true"
- name: APP_INPUT_TI_FILE_PATH
value: "{{inputs.artifacts.ti-artifact.path}}"
- name: APP_INPUT_BACKEND_TI_FILE_PATH
value: "{{inputs.artifacts.backend.path}}"
- name: APP_OUTPUT_FILE_PATH
value: "{{outputs.artifacts.ti-artifact.path}}"In a result, after such step, the artifact will contain not only the
backend.context, but also resolvedvalue.value: # resolved data from backend; will be ignored during TypeInstance upload
resolved: true
bar: baz
backend:
context:
foo: barThe
valueproperty can be used further in workflow, and it will be ignored during the TypeInstance upload/update step.To read more about the TypeInstance Value Fetcher, see the Readme document.
If a given storage backend accept both static value and additional context, then you can specify both
valueandbackend.contextproperties:value: foo
backend:
context:
key: bar
value: baz
You can read more about the storage backends feature here.
Validate the manifests using Capact CLI
You can use the Capact CLI to validate the manifests you created. The capact manifest validate command checks the manifests against JSON schemas and can tell you if your manifests are valid.
For now the Capact CLI does not verify the content of the
actionproperty in Implementations. It will not verify, that your workflow is correct and will execute properly.
To verify all your manifests in manifests directory, execute:
capact manifest validate -r manifests
You can specify an optional flag --server-side flag which will execute additional manifests checks against Capact Hub. As this flag requires connection to an existing Capact installation, ensure that you followed the First use tutorial for CLI.
You can read more about the Capact CLI here.
Populate the manifests into Hub
After we have the manifests ready, populate the manifests to Public Hub.
Create and run your Action
Use the Capact CLI to run your Action.
Export Capact cluster domain name as environment variable:
export CAPACT_DOMAIN_NAME={domain_name} # e.g. capact.localCreate a file with installation parameters:
cat > /tmp/mattermost-params.yaml << ENDOFFILE
input-parameters:
host: mattermost.${CAPACT_DOMAIN_NAME}
ENDOFFILECreate an Action:
capact action create cap.interface.productivity.mattermost.install \
--name mattermost-install \
--parameters-from-file /tmp/mattermost-params.yamlGet the status of the Action from the previous step:
capact action get mattermost-installWait until the Action is in
READY_TO_RUNstate. It means that the Action was processed by the Engine, and the Interface was resolved to a specific Implementation. As a user, you can verify that the rendered Action is what you expected. If the rendering is taking more time, you will see theBEING_RENDEREDphase.note
To automatically wait for
READY_TO_RUN, run:capact act wait --for=phase=READY_TO_RUN mattermost-installRun the Action.
In the previous step, the Action was in the
READY_TO_RUNphase. It is not executed automatically, as the Engine waits for the user's approval. To execute it, execute:capact action run mattermost-installWatch the Action:
capact action watch mattermost-installWait until the Action is finished.
Once the Action is succeeded, view output TypeInstances:
capact action get mattermost-install -ojson | yq e '.Actions[0].output.typeInstances' -
Every output TypeInstance contains the ID of the storage backend used to store its value. You can query the storage backend details with the command capact typeinstance get {id} -oyaml.
View the Action workflow in Argo UI
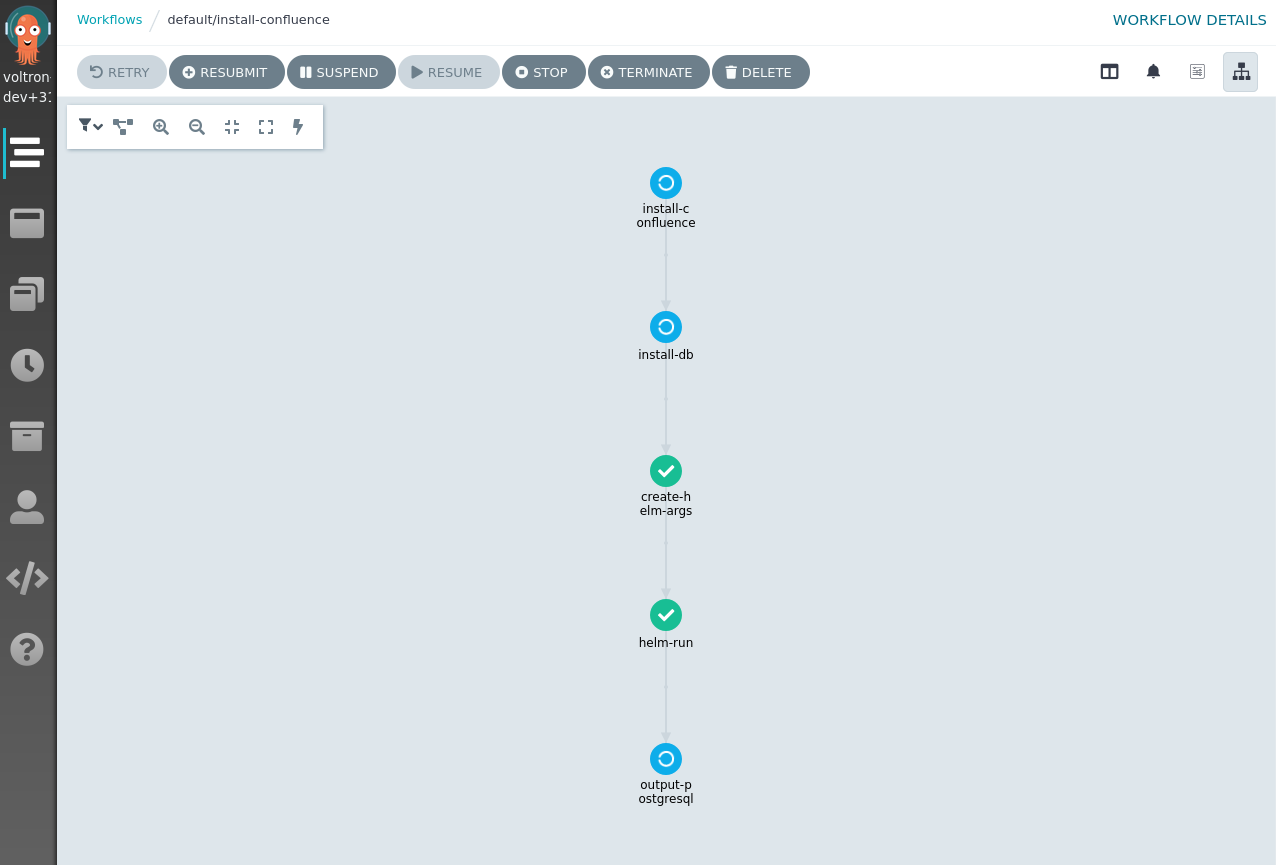
You can also check the status of the Action by monitoring the workflow for the Action on the Argo UI. This can give you useful information, when debugging your Action. To get access to the Argo UI, execute the following command to set up port-forwarding to Argo:
kubectl -n capact-system port-forward svc/argo-argo-workflows-server 2746
Now you can access the Argo UI with your browser by opening http://127.0.0.1:2746.
View the Action Custom Resource
You can also get useful information about your Action using kubectl. You can check the actions.core.capact.io Custom Resource to get information about your Action:
kubectl describe actions.core.capact.io mattermost-install
The output is:
Name: mattermost-install
Namespace: default
Labels: <none>
Annotations: <none>
API Version: core.capact.io/v1alpha1
[...]
Status:
Last Transition Time: 2021-02-08T17:17:27Z
Message: Rendering runner action
Observed Generation: 1
Phase: BeingRendered
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal BeingRendered 3m2s action-controller Rendering runner action
Warning Render runner action 2s (x15 over 2m58s) action-controller while resolving Implementation for Action: while rendering Action: No implementation found for "cap.interface.productivity.mattermost.install"
In the case above, we can see that the action rendering is failing, because the Capact Engine is not able to find the Implementation for cap.interface.productivity.mattermost.install Interface in Hub.
Update TypeInstance
During the Mattermost installation a database user "mattermost" was created. You may want to change the password for this user. Let's do this.
First we need to create an Interface, and a Type for user input:
Type
Input type which just accepts a new password.
manifests/type/database/postgresql/change-password-input.yaml
ocfVersion: 0.0.1
revision: 0.1.0
kind: Type
metadata:
name: change-password-input
prefix: cap.type.database.postgresql
displayName: PostgreSQL change password input
description: Defines PostgreSQL change password input
documentationURL: https://capact.io
supportURL: https://capact.io
maintainers:
- email: [email protected]
name: your-name
url: your-website
spec:
jsonSchema:
value: |-
{
"$schema": "http://json-schema.org/draft-07/schema",
"type": "object",
"title": "The schema for PostgreSQL user input",
"examples": [
{
"password": "some_secret"
}
],
"required": [
"password"
],
"properties": {
"password": {
"$id": "#/properties/password",
"type": "string",
"title": "New user password"
}
},
"additionalProperties": false
}
Interface
It accepts a user input defined earlier and two TypeInstances:
- postgresql - it's needed to get a database address
- user - a database user to changes a password
The Interface outputs modified User TypeInstance, to enable future parent workflows to consume updated password.
manifests/interface/database/postgresql/change-password.yaml
ocfVersion: 0.0.1
revision: 0.1.0
kind: Interface
metadata:
prefix: cap.interface.database.postgresql
name: change-password
displayName: Change user password
description: Action to change a user's password in PostgreSQL
documentationURL: https://www.postgresql.org/docs/
supportURL: https://www.postgresql.org/
iconURL: https://www.postgresql.org/media/img/about/press/elephant.png
maintainers:
- email: [email protected]
name: your-name
url: your-website
spec:
input:
typeInstances:
postgresql:
typeRef:
path: cap.type.database.postgresql.config
revision: 0.1.0
verbs: ["get"]
user:
typeRef:
path: cap.type.database.postgresql.user
revision: 0.1.0
verbs: ["get", "update"] # you need to add "update" verb when you want to update this TypeInstance
parameters:
input-parameters:
typeRef:
path: cap.type.database.postgresql.change-password-input
revision: 0.1.0
output:
typeInstances:
user: # return modified TypeInstance to allow creating parent workflows which use updated values
typeRef:
path: cap.type.database.postgresql.user
revision: 0.1.0
The last step is to create an Implementation. Here we will just use simple postgres container and execute psql binary.
manifests/implementation/postgresql/change-password.yaml
ocfVersion: 0.0.1
revision: 0.1.0
kind: Implementation
metadata:
prefix: cap.implementation.postgresql
name: change-password
displayName: Change PostgreSQL user password
description: Action which changes a PostgreSQL user password
documentationURL: https://www.postgresql.org/docs/
supportURL: https://www.postgresql.org/
license:
name: "Apache 2.0"
maintainers:
- email: [email protected]
name: your-name
url: your-website
spec:
appVersion: "8.x.x"
implements:
- path: cap.interface.database.postgresql.change-password
revision: 0.1.0
requires:
cap.core.type.platform:
oneOf:
- name: kubernetes
revision: 0.1.0
outputTypeInstanceRelations: {}
imports:
- interfaceGroupPath: cap.interface.runner.argo
alias: argo
methods:
- name: run
revision: 0.1.0
- interfaceGroupPath: cap.interface.templating.jinja2
alias: jinja2
methods:
- name: template
revision: 0.1.0
action:
runnerInterface: argo.run
args:
workflow:
entrypoint: main
templates:
- name: main
inputs:
artifacts:
- name: input-parameters
outputs:
artifacts:
- name: user
from: "{{steps.change-password.outputs.artifacts.user}}"
steps:
- - name: prepare-parameters
template: prepare-parameters
arguments:
artifacts:
- name: input-parameters
from: "{{inputs.artifacts.input-parameters}}"
- name: user
from: "{{workflow.outputs.artifacts.user}}"
- name: postgresql
from: "{{workflow.outputs.artifacts.postgresql}}"
- - name: render-change-password-script
capact-action: jinja2.template
arguments:
artifacts:
- name: template
raw:
# Here we prepare a simple script to run the SQL statements to change the user password.
data: |
set -e
export PGPASSWORD=<@user.password@>
PSQL_CMD="psql -h <@postgresql.host@> -U <@user.name@> <@postgresql.defaultDBName@> -c"
${PSQL_CMD} "ALTER USER <@user.name@> WITH PASSWORD '<@input.password@>'"
cat <<EOF > /user.yml
name: <@user.name@>
password: <@input.password@>
EOF
sync
- name: input-parameters
from: "{{steps.prepare-parameters.outputs.artifacts.merged}}"
- name: configuration
raw:
data: ""
- - name: change-password
template: change-password
capact-updateTypeInstances: # here you define that artifact from template `change-password` will be used to update TypeInstance
- name: user
from: user
arguments:
artifacts:
- name: script
from: "{{steps.render-change-password-script.outputs.artifacts.render}}"
- name: change-password
inputs:
artifacts:
- name: script
path: /script.sh
container:
image: postgres:11
command: ["bash", "-c"]
args: ["sleep 1 && chmod +x /script.sh && /script.sh"]
outputs:
artifacts:
- name: user
path: /user.yml
- name: prepare-parameters
inputs:
artifacts:
- name: input-parameters
path: /yamls/input.yaml
- name: user
path: /yamls/user.yaml
- name: postgresql
path: /yamls/postgresql.yaml
container:
image: ghcr.io/capactio/infra/merger:a6e226e
outputs:
artifacts:
- name: merged
path: /merged.yaml
We only updated the user password. Now you need to update the Mattermost settings. At this point you should know how to do this.
Before using the new Interface you again need to populate data with the populator and run a new action. You can use the same GraphQL queries as before. Just change Query Variables:
Create a file with update parameters:
cat > /tmp/update-password.yaml << ENDOFFILE
input-parameters:
password: "new-password"
ENDOFFILECreate a file with input TypeInstances:
cat > /tmp/update-password-tis.yaml << ENDOFFILE
typeInstances:
- name: "postgresql"
id: "<Postgresql TypeInstance ID>"
- name: "user"
id: "<User TypeInstance ID>"
ENDOFFILECreate an Action:
capact action create cap.interface.database.postgresql.change-password \
--name update-password \
--parameters-from-file /tmp/update-password.yaml \
--type-instances-from-file /tmp/update-password-tis.yaml
Summary
In this guide we went through different OCF manifests and their syntax. We created manifests which added a capability to install Mattermost server instances. We also showed, how you can test the manifests you are creating and where to check for useful information, when debugging your action.